Comités municipaux de prévention, atténuation et de réponse des municipalités côtières de San Cristobal, République dominicaine, recevant une formation sur les tsunamis. Décembre 2015.1
Les représentants des comités municipaux pour la prévention des catastrophes, l'atténuation et de réponse (PMR) dans les villes côtières de San Cristobal ont participé au premier atelier de «Formation et renforcement des capacités des institutions de réponse et de soins d'urgence en cas de tsunamis" dans le but d'améliorer la résilience de ces communautés en réponse à la vulnérabilité sismique et aux tsunamis que possède la zone côtière de la République dominicaine.

L'atelier a été organisé en séances séparées, du 8 au 10 Décembre dans les municipalités de Sabana Grande de Palenque, Bajos de Haina et San Gregorio de Nigua, dans le cadre du projet «Actions qui sauvent des vies: la préparation aux catastrophes et la réduction des risque sismiques et du tsunami sur la côte sud ", que dirige le consortium formé par le PNUD, l'UNESCO et l'Assemblée de coopération pour la paix en République Dominicaine (ACPP) et financé par le Programme de préparation aux catastrophes du Service d'aide humanitaire de la Commission européenne (DIPECHO, par son sigle en anglais) dans le cadre du plan 2015-2016 d'action pour les Caraïbes. Ce projet vise à renforcer les capacités de prévention, d'atténuation et d'intervention pour améliorer la résilience des communautés et des institutions dans les municipalités côtières de la province de San Cristobal en cas de séismes et tsunamis, en particulier dans les communes de Bajos de Haina, San Gregorio de Nigua et Sabana Grande de Palenque.
"Les tsunamis sont des événements qui peuvent arriver en République dominicaine et causer des pertes de la vie, des dommages matériels et avoir un impact majeur sur l'économie du pays, il est donc nécessaire de sensibiliser le public et la population en général, et les institutions, afin qu'ils puissent ainsi répondre de manière appropriée en cas de tels événements. Les institutions membres des comités municipaux de prévention, d'atténuation et d'intervention travaillent localement pour réduire les vulnérabilités et dans la réponse d'urgence contre tout phénomène qui peut affecter la population, d'où l'importance de leur formation", explique l'animateur de l'atelier, Jennifer Larreynaga, Consultant UNESCO de l'équipe Action Tsunami et exercice 2016.
Atelier régional de formation sur les tsunamis sur les Centre d'alerte aux tsunamis dans le Pacifique pour GIC / CARIBE-EWS
Cet atelier de formation de quatre jours est organisé par le Centre d'information sur les tsunamis dans les Caraïbes (CTIC) en association avec la COI / UNESCO, le Centre international d'information sur les tsunamis (ITIC), le Centre d'alerte aux tsunamis dans le Pacifique (PTWC), le Programme d'alerte aux tsunamis dans les Caraïbes (CTWP) et l'Unité Gestion de la zone côtière (CZMU), de Barbade. La formation vise 40 participants de 20 pays ainsi que des organisations régionales telles que l'Agence caraïbe de gestion d'urgence des catastrophes (CDEMA), Institut de météorologie et d'hydrologie des Caraïbes (CIMH), CTWP et le Réseau sismique de Porto Rico (PRSN).

L'atelier vise à permettre l’entraînement des Points focaux pour l'alerte aux tsunamis (TWFP), Centre national d'alerte aux tsunamis (NTWC), et les intervenants d'urgence de tsunami (TER) pour effectivement recevoir, analyser et prendre les mesures appropriées de réponse aux produits améliorés de prévision tsunami pour les Caraïbes et les régions adjacentes du Centre d'alerte aux tsunamis dans le Pacifique (PTWC). Cet atelier de formation couvre les opérations d'alerte aux tsunamis et l'utilisation des produits PTWC améliorées pour des prises de décision en cas de menace tsunami, avec une attention particulière sur la chaîne d'alerte aux tsunamis et de leurs Procédures opérationnelles normalisées (SOP). Les sujets traités comprennent l'alerte, les SOP d'intervention et les défis, les outils d'aide à la décision en cas d'alerte, des messages d'avertissement et d'alerte, les concepts d'évacuation et de la planification et des stratégies de sensibilisation.
Au cours des 10+ dernières années, avec des améliorations dans la qualité, la quantité et la disponibilité en temps réel des données, le temps de réponse de PTWC a chuté de manière significative d'une heure à 5-10 minutes pour les tsunamis. Dans le même temps, chaque grand tremblement de terre et tsunami depuis le séisme et le tsunami en de l'océan Indien le 26 Décembre 2004 aident à augmenter la compréhension scientifique, et de meilleures techniques ont été développées pour caractériser rapidement le tremblement de terre et de modéliser numériquement le tsunami.
Dans le Pacifique, le PTWS a adopté le 1er Octobre 2014 l'utilisation des produits améliorés de prévision PTWC basés sur les modèles de prévision numérique. Pour la Caraïbe et les régions adjacentes, le passage aux nouveaux produits améliorés de prévision PTWC a été approuvé par le GIC/CARIBE-EWS VIII (2013 ), introduit au CARIBE WAVE 2013, et depuis le 26 Octobre 2015, sont envoyées en parallèle avec les produits existants. Le passage aux nouveaux produits seuls est prévue pour le 1er Mars 2016.
Remembering the 1945 Makran Tsunami on its 70th Anniversary, 28 November 2015
A magnitude 8.1 earthquake on the morning of 28 November 1945 generated a devastating tsunami that resulted in a loss of life of up to 4,000 people in Pakistan. Archival research has revealed at least five tsunami events in the Makran coastal region from a variety of sources, including earthquakes and landslides.

Recognising the hazard posed by the Makran subduction zone, the countries of the northwest Indian Ocean region, namely, India, Iran, Oman and Pakistan, are organising special events to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the Makran Tsunami on 28 November 2015. Front Cover of the Daily Gazette, Karachi: Thursday, 29 November 1945
• The Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) is organising an exhibition event at their offices in Hyderabad, India.
• The Iranian National Institute for Oceanography and Atmospheric Science (INIOAS) is organising an exhibition event and meeting, inviting universities, research institutes and other organisations as well as the UNESCO Tehran Cluster office and Disaster Management Organisation.
• The Directorate General of Meteorology (DGMET) of Oman is organising an exhibition event during the first week of December.
• UNESCO Office Islamabad, Oxfam GB, NED University, UNDP, National Disaster Management Authority, and Pakistan Meteorological Department are organising an International Conference: “A Step towards Tsunami Resilience” - Commemorating 70th Anniversary of 1945 Makran Tsunami and exhibition in Karachi.
As the memory of the 1945 Makran tsunami fades with the passing of generations, these commemorative events are important to maintain public awareness of the risk of tsunamis in the region. IOC UNESCO has supported the raising of awareness of the Makran hazard through:
• Conducting the project “Communicating the effects of the 1945 Makran tsunami to increase awareness and preparedness of tsunami hazards in the Makran region” with the support of the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia Pacific (UNESCAP). IOC UNESCO published a booklet on remembering the 1945 Makran Tsunami documenting stories of eye-witness accounts of the 1945 tsunami. The booklet is available in Farsi, Urdu, Arabic as well as English. Further information about the results of this project is available on the Indian Ocean Tsunami Information Centre (IOTIC) website: iotic.ioc-unesco.org/1945makrantsunami/.
• Developing and producing the 1945 Makran Tsunami Exhibition panels in Urdu, Farsi, Arabic and English languages with the support of the IOC UNESCO Indian Ocean Tsunami Information Centre (IOTIC).
• Support UNESCO Islamabad Office in developing awareness rising video to remember the 1945 Makran Tsunami to be aired in Pakistan Televisions in relation to the 70th year commemoration of the 1945 Makran Tsunami.
Twelfth Session of the Intergovernmental Coordination Group for the Tsunami Early Warning and Mitigation System in the North-eastern Atlantic, the Mediterranean and Connected Seas (ICG/NEAMTWS-XII)
The Twelfth Session of the Intergovernmental Coordination Group for the Tsunami Early Warning and Mitigation System in the North-eastern Atlantic, the Mediterranean and connected seas (ICG/NEAMTWS) was hosted by the Geological Survey of Ireland from 16–18 November 2015, Dublin.

Participants of the ICG NEAMTWS-XII, Dublin, Ireland, Source: IOC-UNESCO
While tsunamis are less frequent in the North-eastern Atlantic, the Mediterranean and connected seas than in the Pacific and Indian Ocean, the risk of loss of lives and economic disaster in the region is high due to strong population density and infrastructure development along its coasts. The ICG/NEAMTWS was established by Assembly of the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) at its twenty-third session in 2005 by Resolution XXIII-14, with the mandate to coordinate the establishment of a tsunami early warning system for the North-eastern Atlantic, the Mediterranean and connected seas.
Participants reviewed and affirmed the steady progress made in the implementation of the NEAMTWS since its initiation in 2005, particularly the progress achieved by the four Candidate Tsunami Service Providers (CTSPs) in France, Greece, Italy and Turkey. Greece informed ICG/NEAMTWS that its National Observatory of Athens (which acts as a Candidate Tsunami Service Provider) has applied for accreditation. The intention was expressed by France, Italy and Turkey for their respective CTSPs to also apply for accreditation in the next intersessional period.
The Group reviewed the NEAMWave 14 exercise which was conducted from 28-30 October 2014 and its contribution to the implementation of the tsunami warning system for the NEAM region by testing the system in both its up-stream, i.e. tsunami detection, and tsunami alert message delivery, and its down-stream, i.e. the reaction and response components. NEAMWave14, saw a significant increase in the participation of Civil Protection Authorities as compared to NEAMWave 12.
Following the success of the second tsunami exercise for the region, a full-scale exercise named NEAMWave17 is planned in 2017 to test the tsunami readiness of the system and of the Member States.
ICG/NEAMTWS also decided to start conducting quarterly Extended Communication Test Exercises based on a scenario event and encourages Member State Civil Protection Authorities to be involved.
ICG/NEAMTWS recognized the need to continue to exchange information with ICG of the Caribbean Tsunami Early Warning System (ICG/CARIBE-EWS).
The twelfth session of ICG/NEAMTWS was attended by 46 participants from 16 member states and one observer organisation. New officers of ICG/NEAMTWS were elected - Professor Ahmet Yalciner (Turkey) as chair and Dr Anna von Gyldenfeldt (Germany) and Dr Stefano Lorito (Italy) as vice chairs.
The Government of Romania through its National Institute for Earth Physics offered to host the thirteenth session of ICG/NEAMTWS in Bucharest from 26-28 September 2016.
Workshops on Post-IOWave14 Exercise Assessment and Standard Operating Procedures for Tsunami Warning and Emergency Response for India Ocean Countries
ICG/IOTWMS regional training workshops on post-IOWave14 exercise assessment and standard operating procedures (SOPs) were held in Hyderabad, India, 6-10 November 2015, hosted by the Government of India through the Indian Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS). The workshops were attended by twenty-five participants from ten countries, namely: India, Indonesia, Islamic Republic of Iran, Kenya, Malaysia, Maldives, Mauritius, Myanmar, Seychelles and Tanzania. The workshops were conducted by a team of seven trainers from Australia, India, Indonesia, the Indian Ocean Tsunami Information Center and IOC UNESCO.

The workshops targeted Indian Ocean countries that intend to participate down to community level including public evacuations in the IOWave16 exercise, which is scheduled for September 2016. The main objective of the workshops was to develop and integrate SOPs between National Tsunami Warning Centres (NTWCs), National Disaster Management Organisations (NDMOs) and Local Disaster Management Organisations (LDMOs).
The workshop programme included lecture sessions, breakout group work, a tabletop simulation exercise and a site visit to INCOIS, one of the three ICG/IOTWMS Regional Service Providers. Lectures and training material were based on manuals and templates developed by IOC UNESCO in collaboration with the NOAA International Tsunami Information Centre (ITIC) since 2008.
The workshops were followed by ICG/IOTWMS intersessional meetings of its Working Group 2 on Tsunami Detection, Warning and Dissemination and the IOWave16 Task Team on 12-13 November 2015.
Plus d'articles...
Le programme relatif aux tsunamis – ce qu’il est
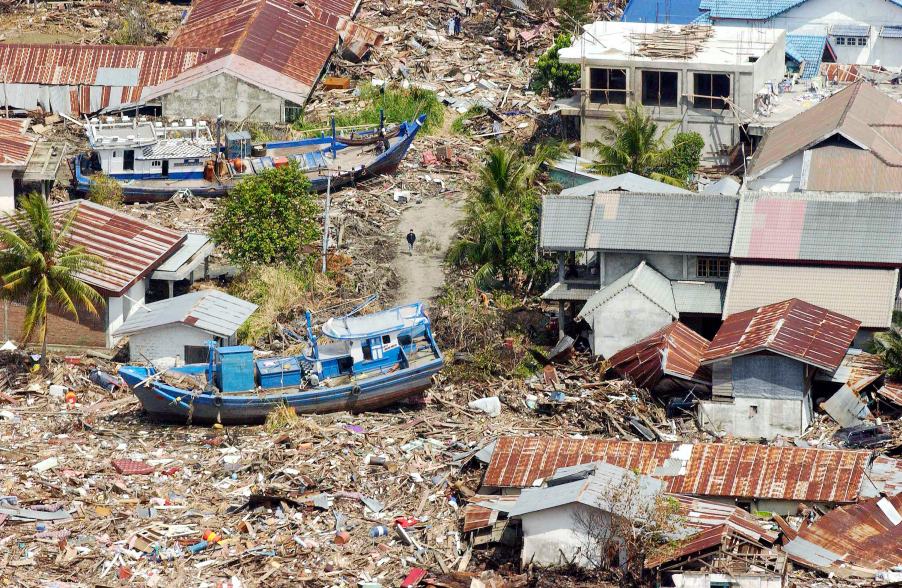

La côte indonésienne, entre Banda Aceh et Meulaboh, au lendemain du tremblement de terre et du tsunami du 26 décembre 2004. Photo Evan Schneider © UN Photo
L’UNESCO aide les États membres à renforcer leur capacité d’évaluation du risque de tsunami, à mettre en œuvre des systèmes d’alerte rapide aux tsunamis et à mieux préparer les populations exposées. Elle travaille étroitement avec les organismes nationaux et favorise la coopération
interorganismes et régionale. Des centres régionaux spécialisés fournissent une information relative aux tsunamis, laquelle, assortie d’une analyse nationale, constitue la base des alertes publiques. En outre, l’UNESCO encourage des démarches fondées sur les populations, à la base, par le biais de l’élaboration de plans d’intervention et de campagnes de sensibilisation qui impliquent fortement les établissements éducatifs et l’utilisateur final.
Upcoming Events
7 August 2024
19 August 2024
19 - 30 August 2024
Chile